Adjuvants classification
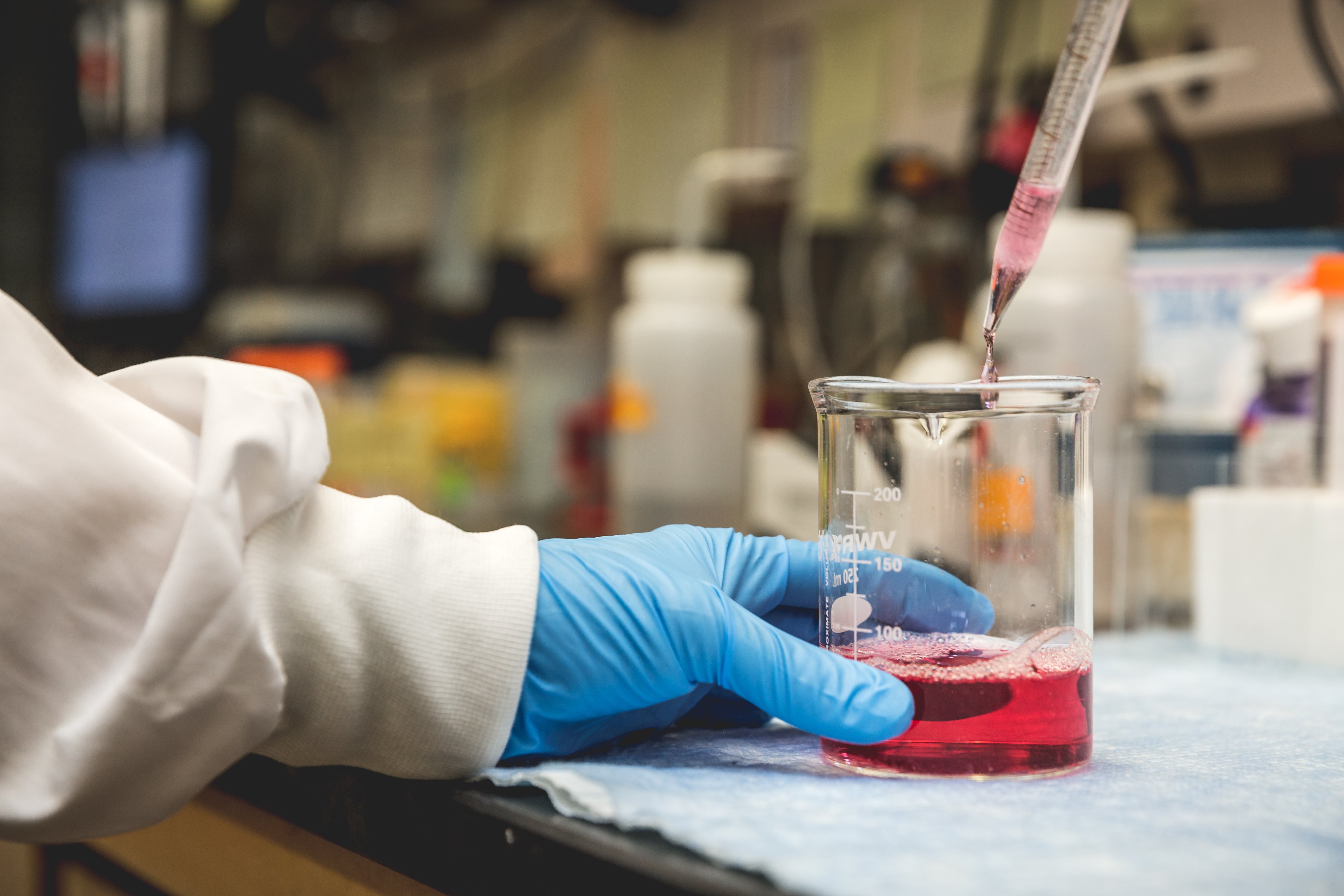 Image credit: Shopify Partners
Image credit: Shopify PartnersAdjuvants
According to wssa an adjuvant for herbicides is a substance present in the formulation of the herbicide or added to the spray tank that will improve the activity of herbicide or improve its application characteristics. There are more than 3000 adjuvants available for use in and these can be classified into:
Activators
They are those that modify the characteristics of the herbicides including particle size, spray curtain viscosity, evaporation rate, etc. The activators are divided into:
Surfactants (SURFAce ACTive AgeNTS) improves the dispersion, emulsification, absorption, spreading, wetting, adhesiveness and/or penetration ability of the applied mixture.
Wetting agents increase the capacity of spray mixtures to remove air or liquids from the surface of the leaves, allowing the spray mixtures to have greater contact with the target.
Oils Increase the retention time of the spray mixtures in the leaves, allowing the increase of the herbicide absorption.
Spray modifiers

Spray modifiers affect the arrival of the drop to the leaf and the deposition of the spray mixtures.
Thickened agents modify the viscosity of the spray mixtures, which can reduce drift and evaporation time after the deposition of the likes in the target.
Adhesive agents increase adhesion, and the ability of the spray mixtures to stick on the leaf surface.
Sprehantes decrease the surface tension of the spray mixtures, making it spread more easily on the leaf surface, forming a thin film covering.
Sprehantes – Adhesives combines the action of the adhesive agent with the Sprehante.
Foaming agents assist in foaming, to reduce drift and evaporation.
Humectants avoid the crystallization of the active ingredient (non-absorbable), keeping the same in solution even after the evaporation of much of the water present in the drop of the deposited spray mixtures.
UV Protectors protect the herbicide from the deleterious effects OF UV rays.
Usage modifiers

They facilitate the management and reduce the problems in herbicide application.
Emulsifiers increase the dispersion between water and oil, creating a more homogeneous mixture.
Disperse breaks the oil phase into smaller parts that mix in water more easily and evenly.
Stabilizing agents increase the viscosity of the final product, increasing the stability of the solution.
Ligating agents generate a chemical bridge between two non-similar materials, usually an inorganic substance and an organic one.
Co-Solvents increases the solubility of a herbicide in water.
Compatibility agents allow the application of two or more active ingredients in the same spraying spray.
Tampon agents alter the PH or hardness of the water to increase the dispersion or solubility of the herbicides in more acidic or basic spray mixtures.
Antifoaming agent reduces foaming in spray mixtures.
Ammonium fertilizers increases herbicide absorption.